Timings: 10:00AM - 5:00PM
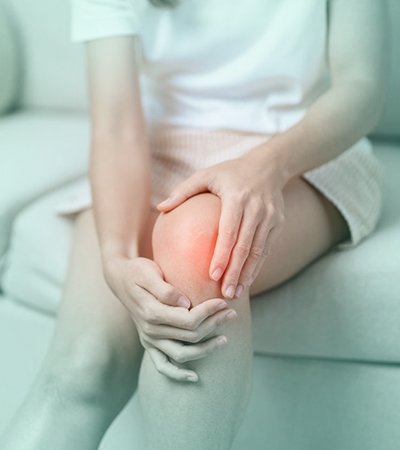
Joint pain can be felt in the joints throughout your body. It may be a symptom of many different health conditions. Arthritis is the most common cause of joint pain. Joint pain may also result from overuse, injury, inflammation, or age-related wear affecting the knees, hips, shoulders, and other joints.
Joint Pain often leads to stiffness, swelling, reduced range of motion, or discomfort during weight-bearing activities. Persistent joint pain can restrict mobility, limit exercise, and affect work or recreational tasks. Early evaluation helps identify structural issues and prevent long-term degeneration.